What is the latest Apache vulnerability (CVE-2019-0211) all about?
The joke was on roughly 2 million servers on Monday (April 1!), as the Apache Foundation released a patch for a privilege escalation bug (CVE-2019-0211) in Apache HTTP Server 2.4 releases 2.4.17–2.4.38. Unfortunately, this is no laughing matter, since this vulnerability makes it possible for module code—software components that enhance the functionality of Apache HTTPD servers—and scripts executed via modules such as mod_php to run code with the privileges of the parent process, which is usually root. This only impacts Apache servers running on UNIX-like systems, which is the majority of them, especially on internet-facing servers.
Is this vulnerability present in your environment? Quickly find out with a free trial of our vulnerability scanner, InsightVM.
Get StartedThis privilege escalation bug is especially problematic for hosting providers that still offer “shared web hosting” plans where a site is running alongside other ones, all of them sharing the same parent Apache server. Even if a vulnerable Apache server is running on its own, this flaw could be used in combination with other attack methods to execute code at a higher privilege level.
How prevalent is the Apache HTTP Server Privilege Escalation vulnerability?
There are 21 separate 2.4.x releases between 2.4.17 and 2.4.38, and Rapid7 Labs Project Sonar harnesses the power of our open source recog utility to fingerprint nodes as we scan them. We found roughly 2 million distinct systems vulnerable to CVE-2019-0211 in our most recent HTTP scans, with 50% of them residing in the “usual suspects” (big cloud-hosting providers).
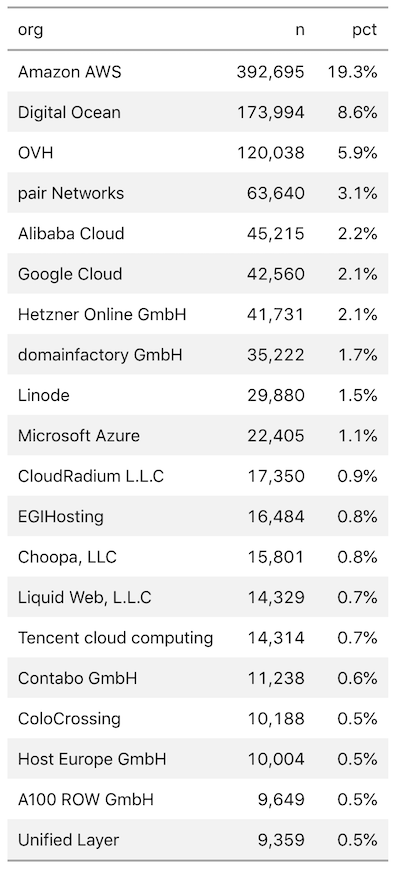
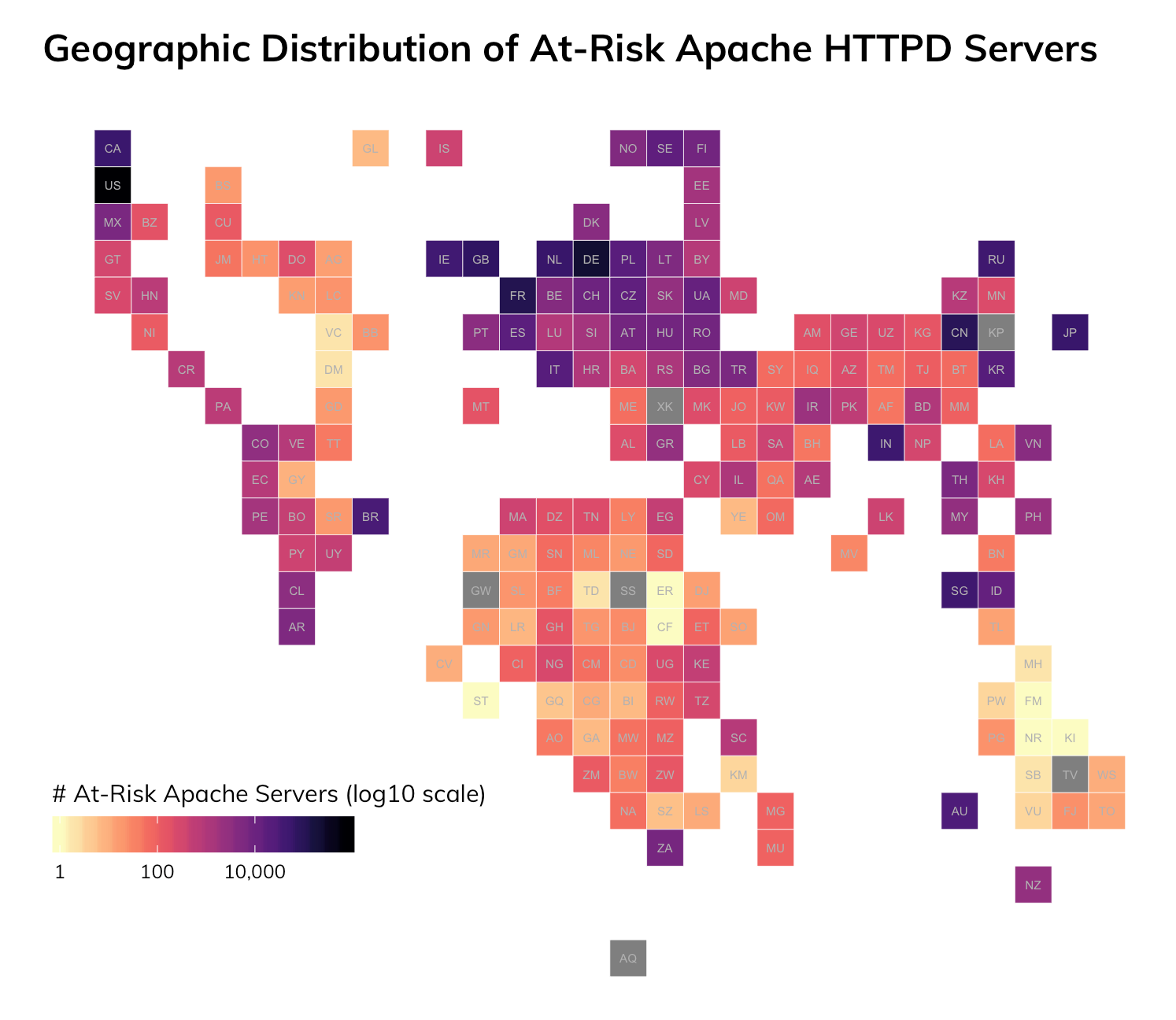
The bulk of affected systems are in the United States (~770,000), Germany (~224,000), and France (~111,000).
What do I do to protect myself from the Apache HTTP Server Privilege Escalation vulnerability?
While this is not a remote code execution (RCE) vulnerability, it does provide a vehicle for attackers to perform actions most hosting providers have worked to avoid. Organizations should consider applying Apache’s fix as soon as possible. And, if organizations host their website(s) in a shared hosting context impacted by this exposure, they should encourage their provider to patch as quickly as possible or consider moving to a different provider/platform.
Rapid7 Labs has no direct reports of any exploitation of this vulnerability but will be working with our external research partners to keep an eye out for active exploits and update this blog if we start to see attacker activity ramp up.
